Project A 3d Vector To Axes
They are always positive and between 0 and 180 inclusive.
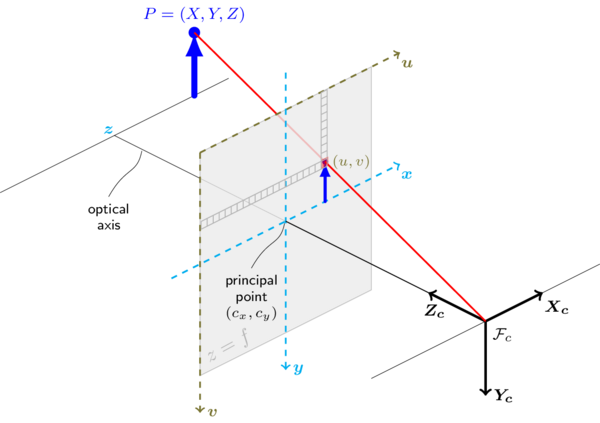
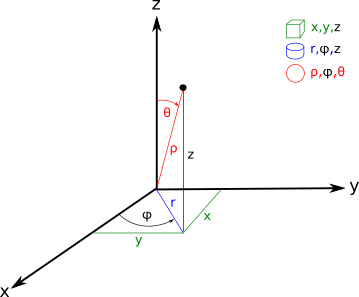
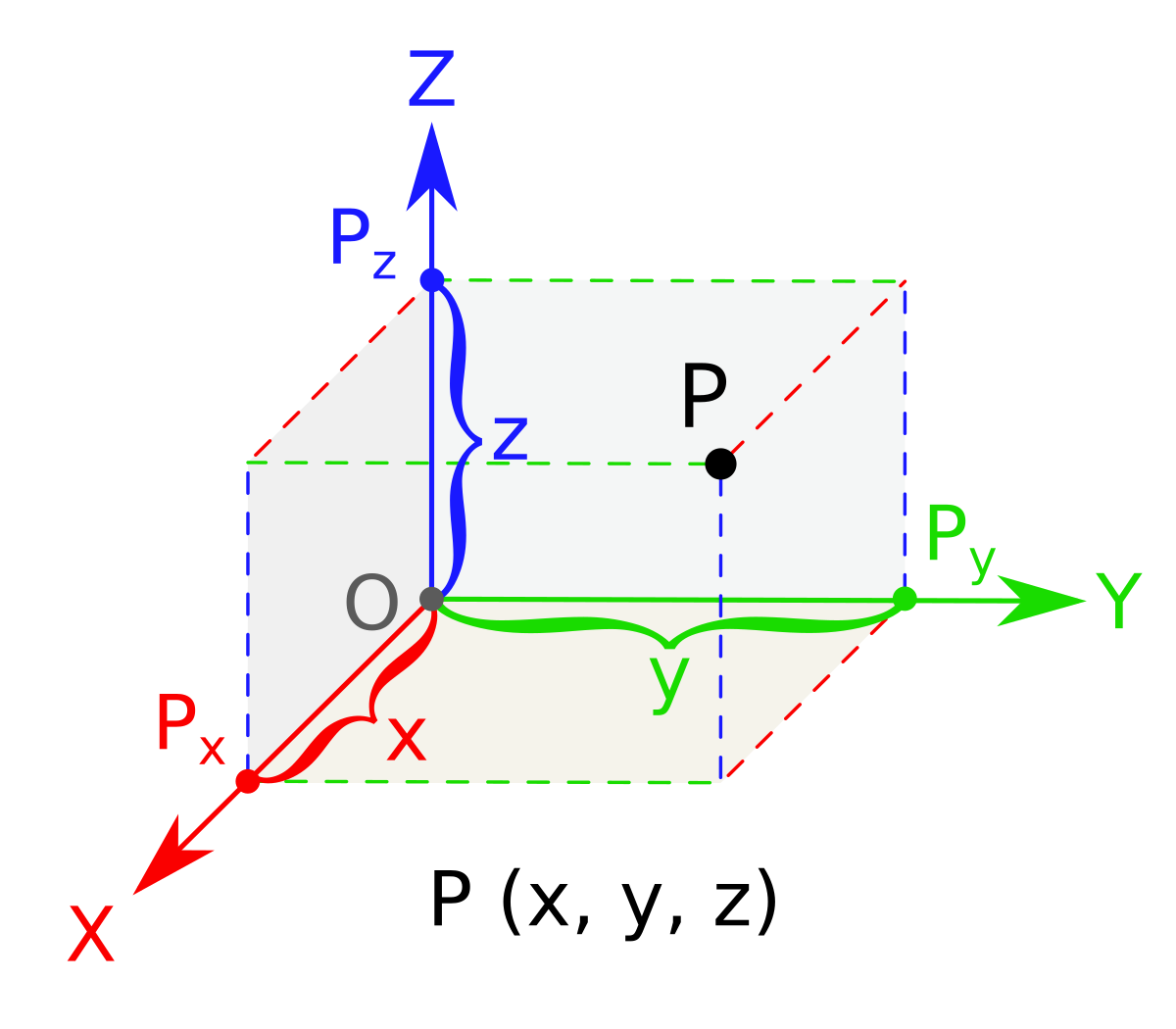
Project a 3d vector to axes. The angle of a 3d vector is the angle from the vector directly to each of the 3 positive axes. Starting with a point which we call the origin construct three mutually perpendicular axes which we call the x axis the y axis and the z axis. Now we extend the idea to represent 3 dimensional vectors using the x y z axes. Suppose we ve already got a vector maybe constructed with cartesian coordinates or retrieved from a pshape.
The vector op has initial point at the origin o 0 0 0 and terminal point at p 2 3 5. To project a vector onto the unit vector a. We saw earlier how to represent 2 dimensional vectors on the x y plane. Here is one way to picture these axes.
The angles are named alpha x axis beta y axis and gamma z axis. We can draw the vector op as follows. It is also used in the separating axis theorem to detect whether two convex shapes intersect. There are no axis specific rotations for 3d.
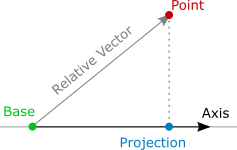
Projection of the vector ab on the axis l is a number equal to the value of the segment a1b1 on axis l where points a1 and b1 are projections of points a and b on the axis l fig. They are called direction angles. Vectors in three dimensional space in three dimensional space there is a standard cartesian coordinate system x y z.